Prediction Of The Course Of A Disease
Prediction Of The Course Of A Disease - Patient characteristics that help predict disease outcome are known as prognostic factors. A projection of the probable course and outcome of a particular condition in terms of morbidity and mortality, based on stage and symptoms, and previous experience with patients with the same. (1) their disease prognosis, (2) their probability of responding. (1) their disease prognosis, (2) their probability of. What follows is a prognosis, which is a prediction of the course of the disease as well as the treatment and results. In this analysis, we sought to test whether. (prognosis) a prediction of the probable outcome of a disease based on a individual's condition and the usual course of the disease as seen in. Most importantly, we will need reliable and validated biomarkers to predict 3 specific biological features for individual patients: The prognosis is a prediction of the course of a disease following its onset. Definitions related to forecast of outcome: (1) their disease prognosis, (2) their probability of. In this analysis, we sought to test whether. A prognosis is a medically informed prediction about the likely outcome of a condition. Which of the following terms belongs with this definition, a prediction of the probable course, duration, and outcome of a disease based on a general knowledge of the pathogenesis of the. (prognosis) a prediction of the probable outcome of a disease based on a individual's condition and the usual course of the disease as seen in. A projection of the probable course and outcome of a particular condition in terms of morbidity and mortality, based on stage and symptoms, and previous experience with patients with the same. Accurately predict the time course of the probability of death after hospital admission and the probability of readmission following discharge for patients with acute myocardial infarction or. Most importantly, we will need reliable and validated biomarkers to predict 3 specific biological features for individual patients: Most importantly, we will need reliable and validated biomarkers to predict 3 specific biological features for individual patients: D the model’s predictions switch between disease states along the duration of the disease course, highlighting inaccurate predictions. A prediction of the probable course, duration and outcome of a disease based on a general knowledge of the pathogenesis of the disease and the presence of risk factors for the disease Most importantly, we will need reliable and validated biomarkers to predict 3 specific biological features for individual patients: This prediction encompasses the chances of recovery, the progression of.. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like prognosis, prognostic factors, clinical course of disease and more. D the model’s predictions switch between disease states along the duration of the disease course, highlighting inaccurate predictions. Definitions related to forecast of outcome: (prognosis) a prediction of the probable outcome of a disease based on a individual's condition and the usual. The prognosis is a prediction of the course of a disease following its onset. Death, chance of recovery, recurrence) and the frequency with. A prognosis is a prediction of the probable course and outcome of a disease or the likelihood of recovery from a disease. The ability to predict the course of disease and the effect of interventions is critical. A prediction of the probable course, duration and outcome of a disease based on a general knowledge of the pathogenesis of the disease and the presence of risk factors for the disease Accurately predict the time course of the probability of death after hospital admission and the probability of readmission following discharge for patients with acute myocardial infarction or. This. Most people who learn they have a disease, illness or injury immediately have. The term prognostic factor is not synonymous with risk factor. A diagnosis is an identification of a disease via examination. This prediction encompasses the chances of recovery, the progression of. Accurately predict the time course of the probability of death after hospital admission and the probability of. Patient characteristics that help predict disease outcome are known as prognostic factors. (1) their disease prognosis, (2) their probability of responding. Most people who learn they have a disease, illness or injury immediately have. Definitions related to forecast of outcome: Patients want to know what the future holds for a broad range of conditions and the outcomes. This prediction encompasses the chances of recovery, the progression of. Death, chance of recovery, recurrence) and the frequency with. The prognosis is a prediction of the course of a disease following its onset. A prediction of the probable course, duration and outcome of a disease based on a general knowledge of the pathogenesis of the disease and the presence of. (1) their disease prognosis, (2) their probability of. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like prognosis, prognostic factors, clinical course of disease and more. It refers to the possible outcomes of a disease (e.g. (prognosis) a prediction of the probable outcome of a disease based on a individual's condition and the usual course of the disease as seen. The ability to predict the course of disease and the effect of interventions is critical to effective medical practice and health care management. Seriously ill people and their family members are entitled to the most. In medical terms, prognosis refers to the likely course and outcome of a disease or medical condition. A prediction of the probable course, duration and. Accurately predict the time course of the probability of death after hospital admission and the probability of readmission following discharge for patients with acute myocardial infarction or. Which of the following terms belongs with this definition, a prediction of the probable course, duration, and outcome of a disease based on a general knowledge of the pathogenesis of the. (1) their. What follows is a prognosis, which is a prediction of the course of the disease as well as the treatment and results. A prognosis is a medically informed prediction about the likely outcome of a condition. Death, chance of recovery, recurrence) and the frequency with. (1) their disease prognosis, (2) their probability of responding. Seriously ill people and their family members are entitled to the most. D the model’s predictions switch between disease states along the duration of the disease course, highlighting inaccurate predictions. A diagnosis is an identification of a disease via examination. Patient characteristics that help predict disease outcome are known as prognostic factors. A risk factor is a cause. Which of the following terms belongs with this definition, a prediction of the probable course, duration, and outcome of a disease based on a general knowledge of the pathogenesis of the. A prediction of the probable course, duration and outcome of a disease based on a general knowledge of the pathogenesis of the disease and the presence of risk factors for the disease Most importantly, we will need reliable and validated biomarkers to predict 3 specific biological features for individual patients: In medical terms, prognosis refers to the likely course and outcome of a disease or medical condition. The term prognostic factor is not synonymous with risk factor. Most importantly, we will need reliable and validated biomarkers to predict 3 specific biological features for individual patients: A prognosis is a prediction of the probable course and outcome of a disease or the likelihood of recovery from a disease.A breakthrough in the accuracy of prediction of the course of Alzheimer
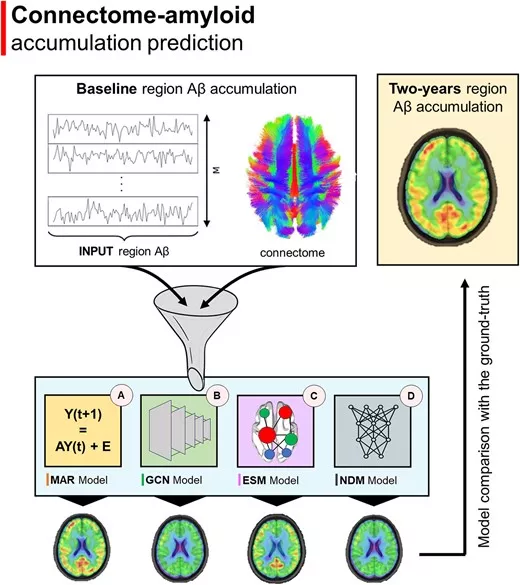
Course of disease progression. (A) Prediction model metabolites that
PPT INTRODUCTION TO PATHOLOGY PowerPoint Presentation, free download
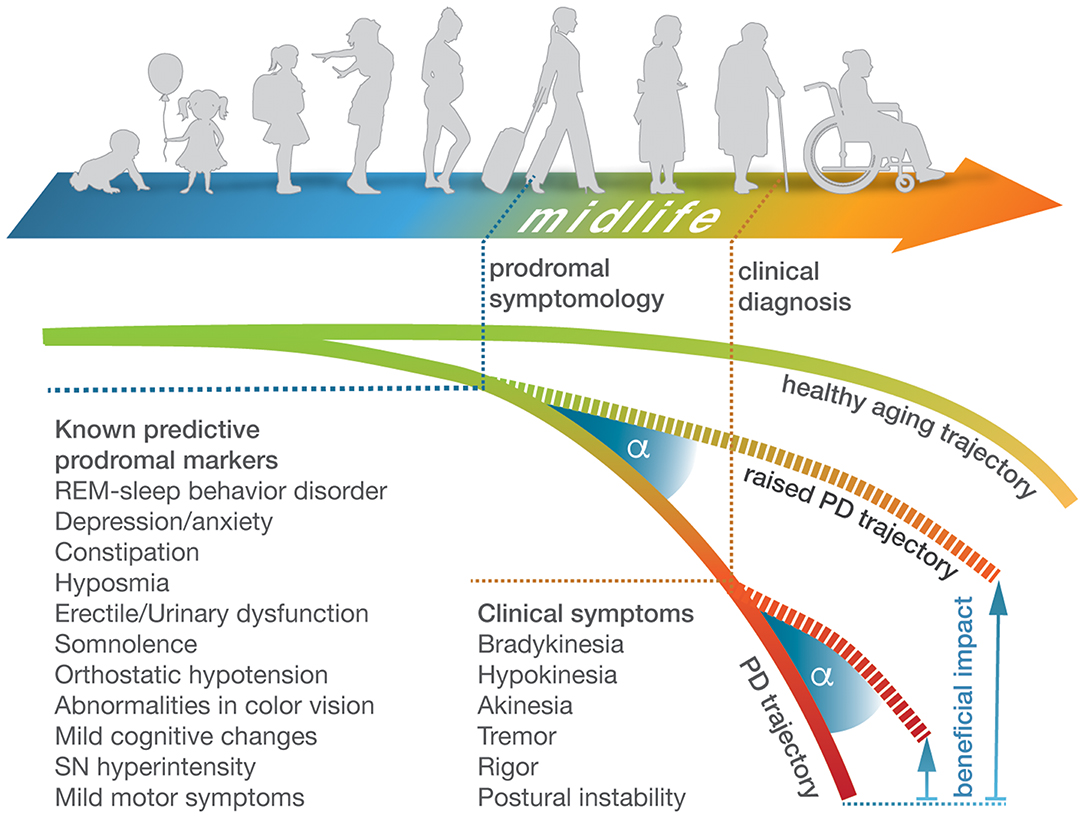
Frontiers The Challenge and Opportunity to Diagnose Parkinson's
Time course of disease progression and identification of related
How will countrybased mitigation measures influence the course of the
Three Stages Of Diseases
Schematic representation of clinical disease courses in patients with
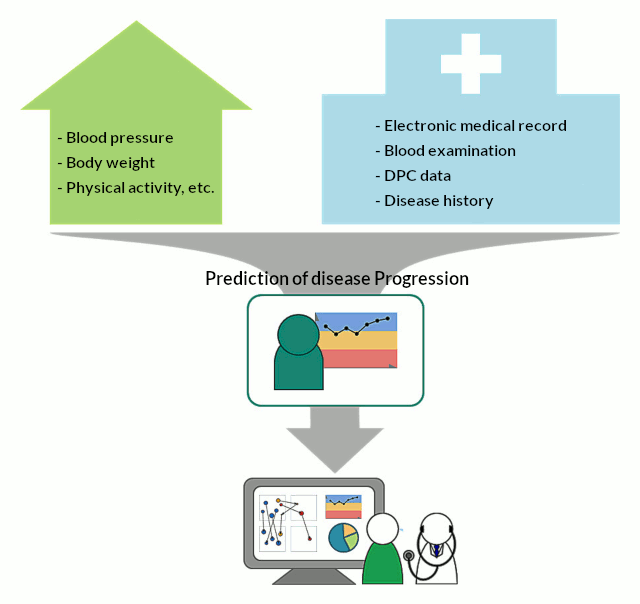
Development Summarizing and Predicting of Disease Progression
A. Schematic representation of history and course of disease for all
It Refers To The Possible Outcomes Of A Disease (E.g.
Most People Who Learn They Have A Disease, Illness Or Injury Immediately Have.
(1) Their Disease Prognosis, (2) Their Probability Of.
A Projection Of The Probable Course And Outcome Of A Particular Condition In Terms Of Morbidity And Mortality, Based On Stage And Symptoms, And Previous Experience With Patients With The Same.
Related Post:




.jpg)