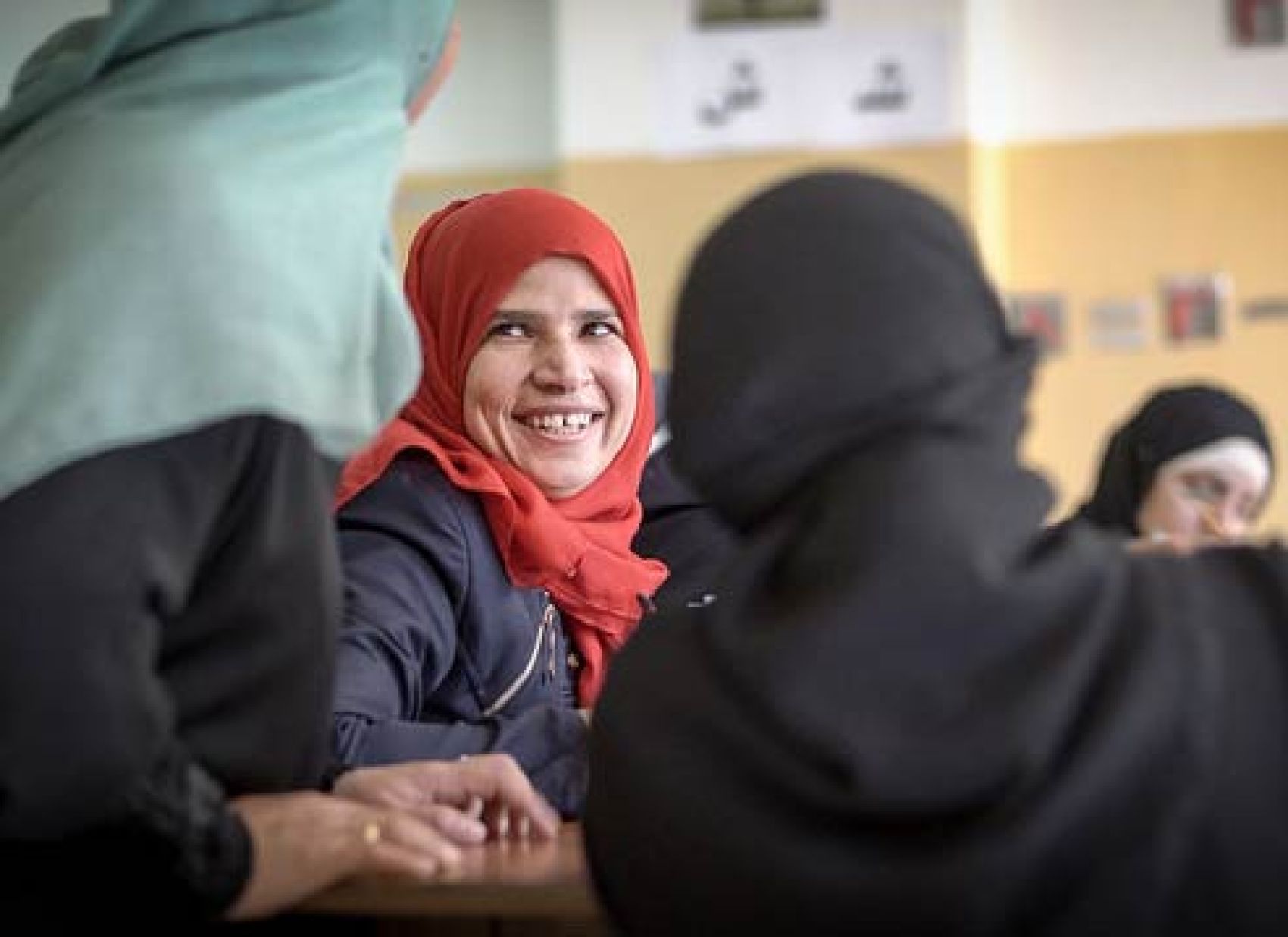
Throughout The Life Course Gender Shapes
Throughout The Life Course Gender Shapes - What is the form of social organization. We’ll dig into examples of gender performances, sexual identities, intersectional. All societies define masculinity in. How do gender gaps accumulate and persist from childhood to older age? Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like margaret mead's research on gender in three societies in new guinea illustrates that: The impact of social determinants on health. Evidence from the israeli kibbutzim suggests that cultures have the ability to define what is masculine and feminine in various ways. We highlight how women are financially, physically, and mentally. How do cultural prescriptions and social structure combine with biology to shape the distinctive aging process of men and. All of the above, 2). Levels of social isolation increase from adolescence through later life for both men and women. We’ll dig into examples of gender performances, sexual identities, intersectional. In what ways does gender—as it intersects with race, ethnicity, social class, and sexual identity—shape these life course processes, even as it is shaped by them? Social isolation increases for everyone over the life course: Margaret mead argued that gender was mostly a. 4 elder argued that four key components impact human. This web page presents data and analysis on education, work, care, and pension outcomes for women and. Gender plays a crucial role in shaping life course transitions, influenced by societal norms and cultural expectations. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like margaret mead's research on gender in three societies in new guinea illustrates that: Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like 1) throughout the life course, gender shapes: Which concept refers to attitudes and activities that a society links to people of each sex?. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like 1) throughout the life course, gender shapes: Following a brief history of the life course perspective on sexualities, the author outlines a conceptual framework for studying gendered sexualities from birth to death. Social isolation increases. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like throughout the life course, gender shapes:, when did feminism as a social movement in the united states begin?,. We’ll dig into examples of gender performances, sexual identities, intersectional. Throughout the life course, gender shapes _____ select one: Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like margaret mead's research on gender. From childhood to old age, these roles dictate the. How do gender gaps accumulate and persist from childhood to older age? Throughout the life course, gender shapes ________ human feelings, thoughts, and actions. This web page presents data and analysis on education, work, care, and pension outcomes for women and. Levels of social isolation increase from adolescence through later life. In what ways does gender—as it intersects with race, ethnicity, social class, and sexual identity—shape these life course processes, even as it is shaped by them? We propose a measure of gender segregation over the life course that includes differences between women and men in occupational allocation, degree of time involvement in paid work,. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards. Gender plays a crucial role in shaping life course transitions, influenced by societal norms and cultural expectations. Clarity of the concept of gender is very important to understand the life course in a gendered perspective. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like 1) throughout the life course, gender shapes: In this course, we’ll explore some of the ways. We’ll dig into examples of gender performances, sexual identities, intersectional. 4 elder argued that four key components impact human. The complex life course etiology of chronic diseases that typically manifests later in life but has its roots in young adulthood. How do cultural prescriptions and social structure combine with biology to shape the distinctive aging process of men and. Study. What is feminine to one society may be masculine to another. Throughout the life course, gender shapes _____ select one: Social isolation increases for everyone over the life course: What is the form of social organization. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like margaret mead's research on gender in three societies in new guinea illustrates that: We’ll dig into examples of gender performances, sexual identities, intersectional. From childhood to old age, these roles dictate the. All societies define masculinity in. How do cultural prescriptions and social structure combine with biology to shape the distinctive aging process of men and. Following a brief history of the life course perspective on sexualities, the author outlines a conceptual framework. The complex life course etiology of chronic diseases that typically manifests later in life but has its roots in young adulthood. 4 elder argued that four key components impact human. In what ways does gender—as it intersects with race, ethnicity, social class, and sexual identity—shape these life course processes, even as it is shaped by them? Therefore, it is pertinent. Gender plays a crucial role in shaping life course transitions, influenced by societal norms and cultural expectations. What is feminine to one society may be masculine to another. Following a brief history of the life course perspective on sexualities, the author outlines a conceptual framework for studying gendered sexualities from birth to death. How do cultural prescriptions and social structure. We’ll dig into examples of gender performances, sexual identities, intersectional. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like 1) throughout the life course, gender shapes: Age, gender and sexuality through the life course argues that the gendered structure of temporality (defined in the dual sense of everyday time as well as age and stage. All societies define masculinity in. Throughout the life course, gender shapes _____ select one: The impact of social determinants on health. We propose a measure of gender segregation over the life course that includes differences between women and men in occupational allocation, degree of time involvement in paid work,. Gender plays a crucial role in shaping life course transitions, influenced by societal norms and cultural expectations. What is feminine to one society may be masculine to another. Margaret mead's research on gender in three societies in new guinea illustrates that: In what ways does gender—as it intersects with race, ethnicity, social class, and sexual identity—shape these life course processes, even as it is shaped by them? Therefore, it is pertinent to consider how structural sexism shapes women’s health throughout the life course. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like throughout the life course, gender shapes:, when did feminism as a social movement in the united states begin?,. We highlight how women are financially, physically, and mentally. From childhood to old age, these roles dictate the. Which concept refers to attitudes and activities that a society links to people of each sex?.Closing gender gaps throughout the life course Human Development Reports
Gender Socialization Ppt Powerpoint Presentation Model Shapes Cpb
Alexandra Y. Aikhenvald How Gender Shapes The WorldOxford University
Health matters Prevention a life course approach GOV.UK
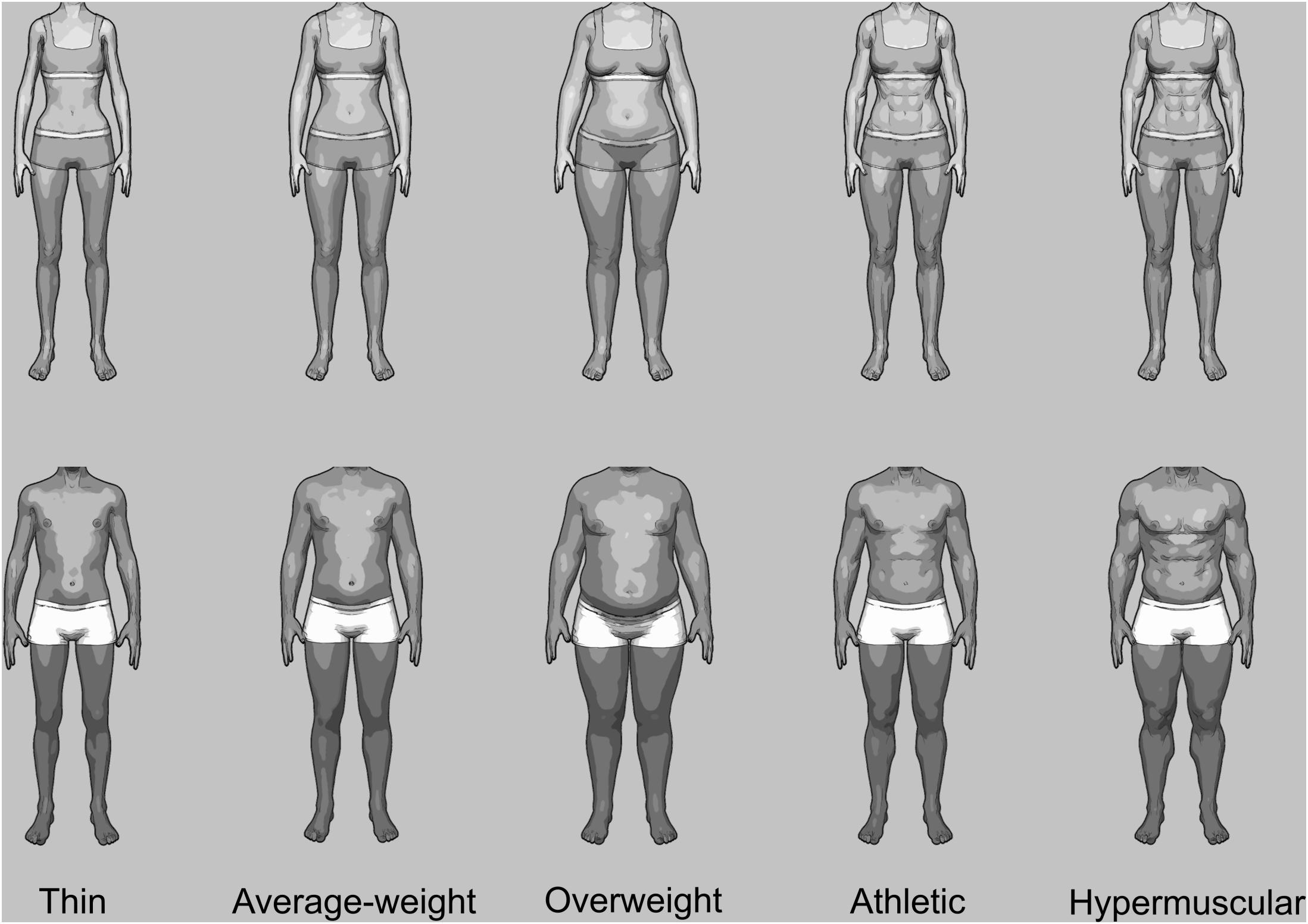
Frontiers Gender Differences in Body Evaluation Do Men Show More
Solved Throughout the life course, gender shapesa) human
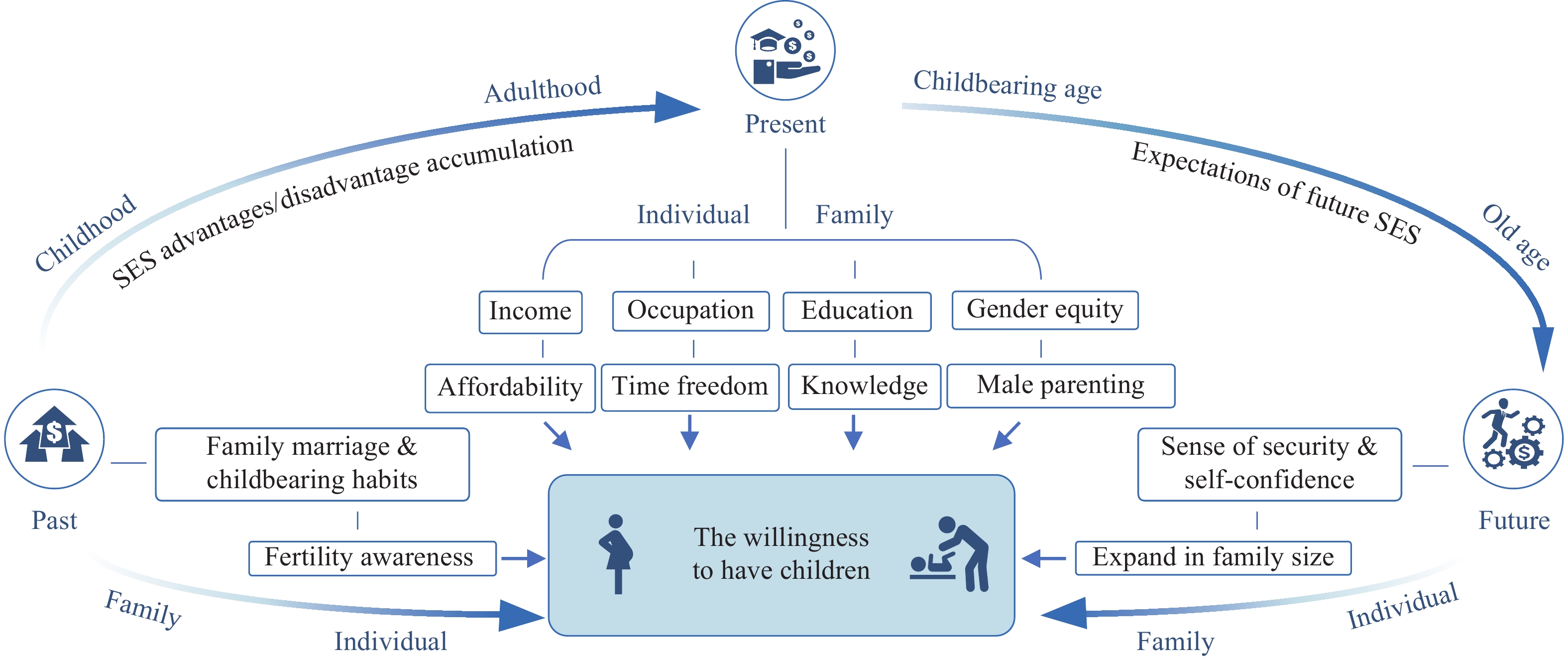
Expectations of Improvement of Socioeconomic Status Throughout the Life
Gender Socialization throughout the Life Course SALTISE
Socialization And The Life Course YouTube
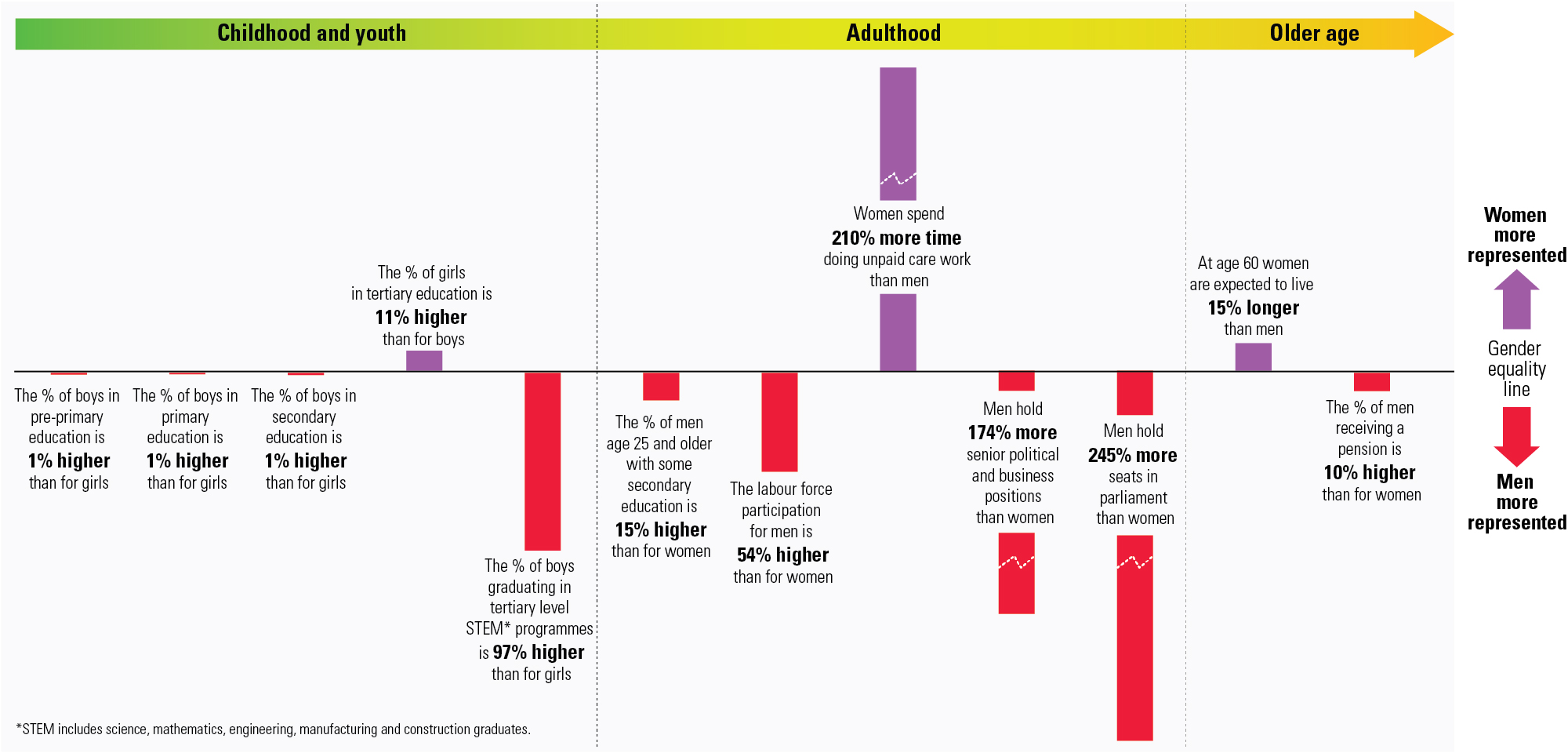
Closing gender gaps throughout the life course Human Development Reports
Levels Of Social Isolation Increase From Adolescence Through Later Life For Both Men And Women.
Study With Quizlet And Memorize Flashcards Containing Terms Like Margaret Mead's Research On Gender In Three Societies In New Guinea Illustrates That:
What Is The Form Of Social Organization.
Margaret Mead Argued That Gender Was Mostly A.
Related Post: