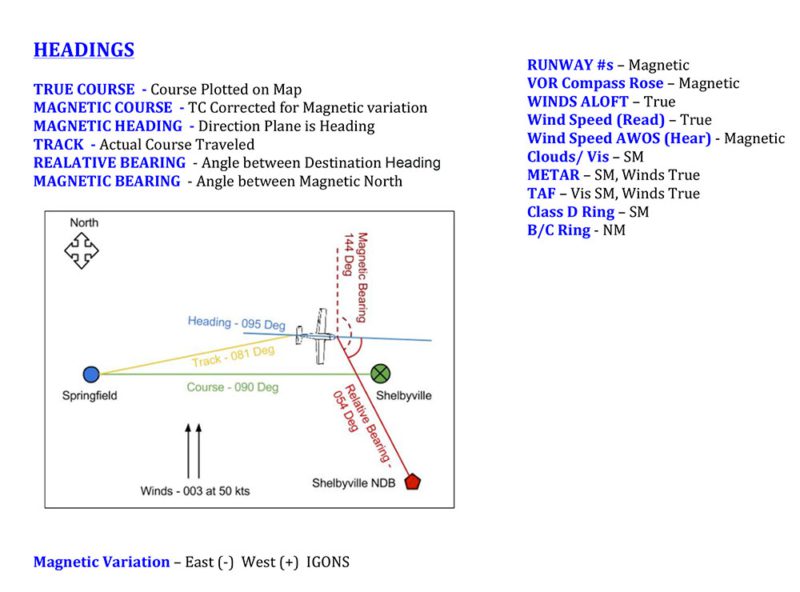
What Is True Course
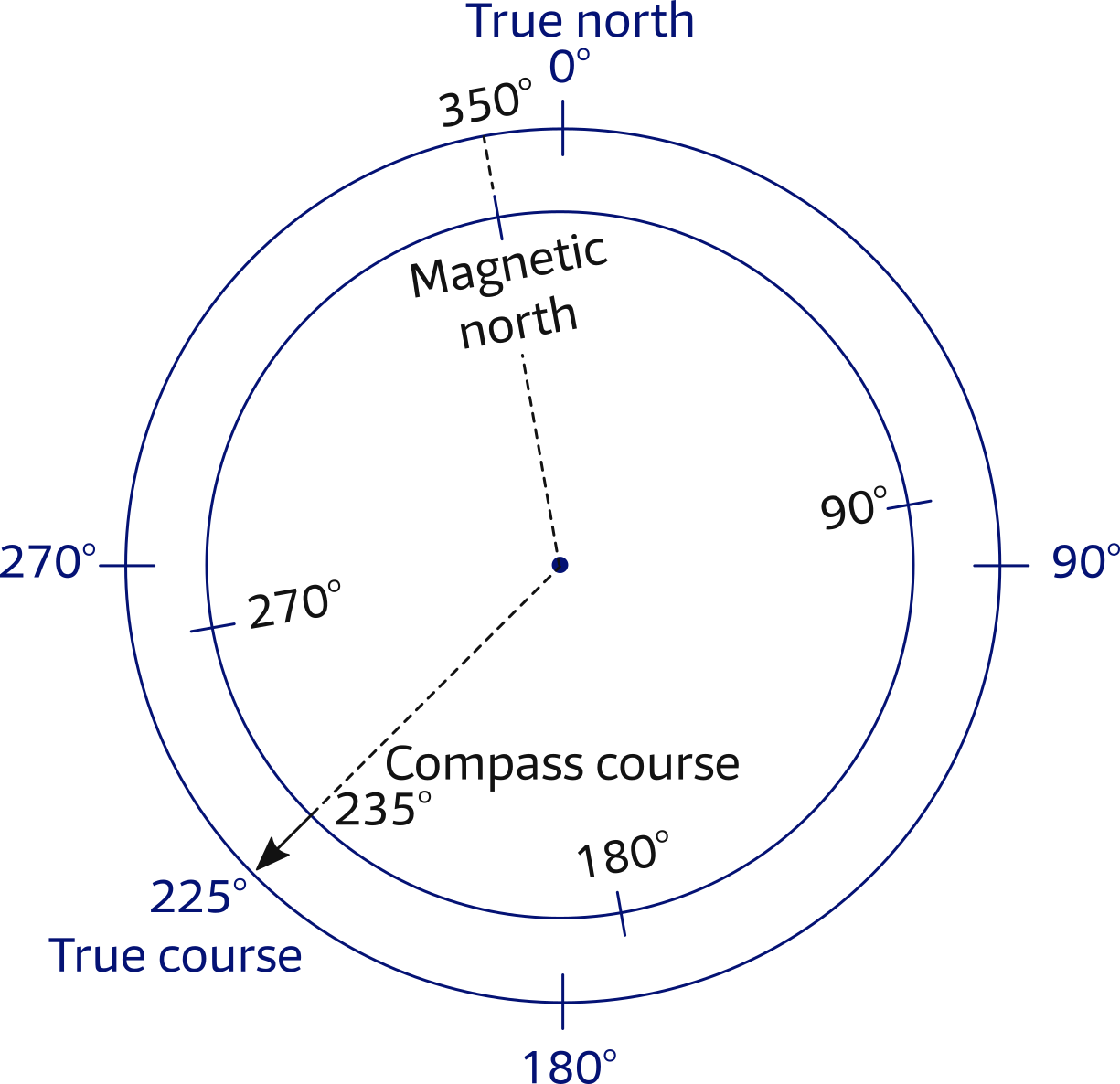
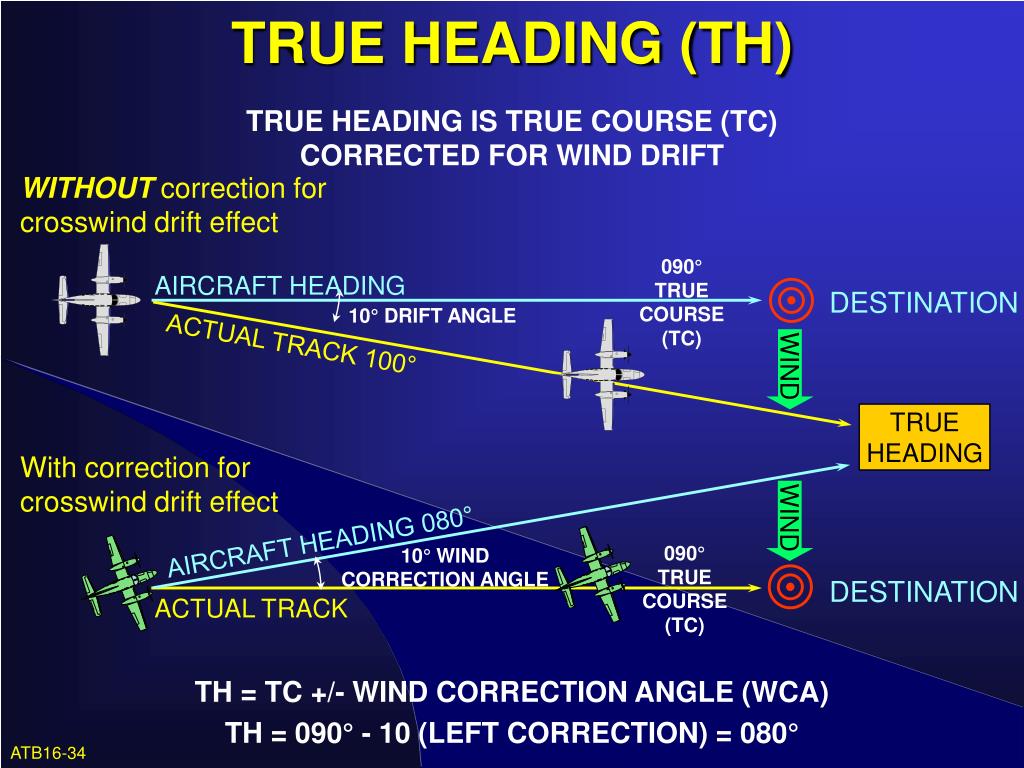
What Is True Course - True course (tc) is the direction or heading you calculate when plotting your flight's route on a sectional chart using a navigation plotter. A true heading is the course corrected for. The true course refers to the planned or intended direction of travel, expressed in degrees relative to true north (the geographic north pole). It is measured from the geographic (or magnetic) north in. A true course is a heading based on the direction you intend to travel. Magnetic heading is your direction relative to magnetic north, read from your magnetic compass. A ship’s true course is determined by the direction from the ship to the geographic north pole (also called true north). The aircraft's course over the ground relative to true north. Magnetic heading is your your true course. The true course is the aircraft path over the ground referenced to true north. This video explains how direction is measured on earth and the concepts of true course (tc), magnetic variation and magnetic course (mc) with graphical examp. True heading is your direction relative to true north, or the geographic north pole. Magnetic heading is your direction relative to magnetic north, read from your magnetic compass. Remember that because of the projection of the map, it. A true course is a heading based on the direction you intend to travel. Students at arizona state university love the dreamscape learn virtual reality biology experiences, and the intense engagement it creates is leading to higher grades and. Magnetic heading is your your true course. Here is a cheat sheet showing the difference between true course, headings, & bearings along with a list of what is described in magnetic verses true, and statute miles (sm). It is defined as the angle between the aircraft's longitudinal axis and a. A ship’s true course is determined by the direction from the ship to the geographic north pole (also called true north). This is the course measured from your navigation plotter when you plot your flight on your map. True course is measured with a navigation plotter and a sectional map. The aircraft's course over the ground relative to true north. You'll get the most accurate tc if you measure it in. True course (tc) is the direction or heading you calculate. A ship’s true course is determined by the direction from the ship to the geographic north pole (also called true north). It is the direction in which the vessel or. True course (tc) is the direction or heading you calculate when plotting your flight's route on a sectional chart using a navigation plotter. A true heading is the course corrected. The aircraft's course over the ground relative to true north. A ship’s true course is determined by the direction from the ship to the geographic north pole (also called true north). Magnetic heading is your your true course. Magnetic heading is your direction relative to magnetic north, read from your magnetic compass. True course (tc) refers to the actual direction. It is the direction in which the vessel or. True course (tc) refers to the actual direction a pilot or navigator must follow to reach their intended destination. Magnetic heading is your your true course. The true course is the aircraft path over the ground referenced to true north. The true heading in the direction the aircraft nose is pointing. The tariff backstory for individual purchases we’re considering making is arguably a more valuable data point than a superficial, potentially misleading “made in the u.s.a.” or. You'll get the most accurate tc if you measure it in. This video explains how direction is measured on earth and the concepts of true course (tc), magnetic variation and magnetic course (mc) with. Magnetic heading is your direction relative to magnetic north, read from your magnetic compass. The true course is the aircraft path over the ground referenced to true north. Navigation charts and the compass are labeled with true north, but setting a. This is the course measured from your navigation plotter when you plot your flight on your map. Students at. The true course refers to the planned or intended direction of travel, expressed in degrees relative to true north (the geographic north pole). You'll get the most accurate tc if you measure it in. This is the course measured from your navigation plotter when you plot your flight on your map. Navigation charts and the compass are labeled with true. True course is measured with a navigation plotter and a sectional map. Magnetic heading is your direction relative to magnetic north, read from your magnetic compass. The true course is the aircraft path over the ground referenced to true north. The true course refers to the planned or intended direction of travel, expressed in degrees relative to true north (the. Here is a cheat sheet showing the difference between true course, headings, & bearings along with a list of what is described in magnetic verses true, and statute miles (sm). Students at arizona state university love the dreamscape learn virtual reality biology experiences, and the intense engagement it creates is leading to higher grades and. The tariff backstory for individual. It is the direction in which the vessel or. True course (tc) refers to the actual direction a pilot or navigator must follow to reach their intended destination. It might be the same as your magnetic heading in perfect conditions, with no winds. The difference between the two results from a crosswind, which may require you to fly a different. True course (tc) is the direction or heading you calculate when plotting your flight's route on a sectional chart using a navigation plotter. The difference between the two results from a crosswind, which may require you to fly a different true heading to achieve your true course. Navigation charts and the compass are labeled with true north, but setting a. True course) would be the angle in degrees between the true or geographic north and the course. It is measured from the geographic (or magnetic) north in. Here is a cheat sheet showing the difference between true course, headings, & bearings along with a list of what is described in magnetic verses true, and statute miles (sm). In this insightful lawyers who learn episode, david schnurman, ceo of lawline, has a conversation with drew amoroso, founder of duecourse,. True course (tc) refers to the actual direction a pilot or navigator must follow to reach their intended destination. You'll get the most accurate tc if you measure it in. It is defined as the angle between the aircraft's longitudinal axis and a. The true course is the aircraft path over the ground referenced to true north. Students at arizona state university love the dreamscape learn virtual reality biology experiences, and the intense engagement it creates is leading to higher grades and. Magnetic heading is your direction relative to magnetic north, read from your magnetic compass. True course is measured with a navigation plotter and a sectional map. A true course is a heading based on the direction you intend to travel. It is the direction in which the vessel or.HOW TO SOLVE TRUE COURSE YouTube
Heading, Course, Bearing, True Blonds In Aviation
True Course vs True Heading vs (How Are They Different?)
True Course vs True Heading vs (How Are They Different?)
True Course vs True Heading vs (How Are They Different?)
Aircraft Maneuvers STK Components for 2021 r2
Enriching an NMEA Stream
Marine navigation courses compass ASA RYA
True and Course Courses and Headings in Navigation (Part 1/2
PPT Let’s see… Shall I navigate today by... PowerPoint Presentation
True Heading Is Your Direction Relative To True North, Or The Geographic North Pole.
A Ship’s True Course Is Determined By The Direction From The Ship To The Geographic North Pole (Also Called True North).
The Aircraft's Course Over The Ground Relative To True North.
A True Heading Is The Course Corrected For.
Related Post: